Richard D. Powell, PhD
Research Director
Advanced
Technical Support
Custom Synthesis Consulting
Selected Publications
Email: rpowell@nanoprobes.com
Research Interests
Many of these activities are supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation through the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program.
Combined Fluorescent and Gold Labeling
Fluorescence and electron microscopies are two complementary techniques: therefore, the data which each one yields about what is happening in a biological system is quite different. We have attached both a gold cluster and a fluorophore to a single Fab' fragment to yield a probe which may be used to localize its targets using either method, and researchers using this probe have imaged labeled cells by fluorescence microscopy, light microscopy in a variety of imaging modes, and electron microscopy. Both the global distribution or the movement of an antigen within entire cells (including living cells), and antigen localization at the macromolecular level may be obtained from a single labeling procedure. Because fluorophores come in different colors, a greater number of different antigens may be labeled and distinguished in one sample. Our FluoroNanogold probes were developed from this research.
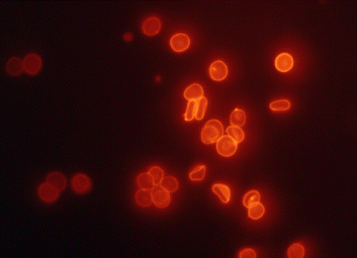
Suspended sheep red blood cells labeled with polyclonal rabbit anti-sheep RBC primary antibody, followed by a combined Cy3/Nanogold-labeled goat Fab' anti-rabbit IgG secondary probe. Original magnification X 1,000, viewed using rhodamine filter set.
Our collaborations include Dr. David Spector at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, who used our probes to identify components of RNA splicing sites in cells. The Biomedical Imaging Group, and Dr. Roger Craig of the Cell Biology Department at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center used these new probes with fluorescence deconvolution and electron microscopy to study the mechanisms of signal transduction in smooth muscle cells, and Dr. Andrew Belmont at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign is also using the new probes to investigate the structure of nuclear components.
Large Metal Cluster and Cluster Polymer Immunoprobes
Nanogold® is the largest gold cluster so far, but it is too small for many applications because it requires silver enhancement to be visualized against some stains. This project uses two approaches to solving this problem: (a) larger cluster complexes, up to 3 nm, which are formed by other metals such as palladium and platinum; and (b) multiple gold cluster complexes linked to compact, branched-chain polymers. Dr. David Spector of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory is collaborating with us on electron microscopy of the new probes. We are also investigating whether such probes can be used to increase the sensitivity of immunoassay systems, and in collaboration with United Biomedical, Incorporated of Hauppauge, NY, we are developing their applications to medical diagnostics.
Caged Metal Cluster and Colloid Immunoprobes
The preparation of single-particle, covalently linkable immunoelectron microscopy labels greater than 3.6 nm cannot be achieved using any existing metal cluster complexes, since none are known larger than 3.6 nm in diameter. As an alternative, we are investigating control of the size, surface properties and cross-linking functionalities of larger colloidal particles, and cluster complexes enlarged by autometallography, (a) by using either ligand complements which restrict the growth of these particles, or (b) by preparing the metal particles inside existing cage-like molecules which restrict their growth to a desirable size. Dr. David Spector of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory will use the smaller labeled probes to study the mammalian cell nucleus, while the larger probes will be used by Dr. Peter Takvorian in collaboration with Prof. Ann Cali of The Biological Sciences Center at Rutgers University to study the structural features of microsporidia associated with opportunistic infections related to the HIV virus.
New ways to conjugate and target gold cluster labels
The range of chemistry available to link our metal clusters to other molecules offers many routes to new labeled probes, and of incorporating novel mechanisms to target these labels to sites of interest. For example, gold clusters can be inserted into synthetic peptides or oligonucleotides during solid-phase synthesis by using gold-labeled monomers.This opens up possibilities such as incorporating highly visible tags selectively into combinatorial arrays, or the direct synthesis of labeled in situ hybridization probes. We are also preparing gold conjugates with much smaller probes such as biotin or phalloidin.
Another method for targeting is to use the nickel (II) chelate of nitrilotriacetic acid, which has a high affinity for polyhistidine sequences. We have prepared gold cluster probes in which the NTA-Ni(II) moiety is incorporated into the cluster, as shown below, and used to label polyhistidine sequences engineered into the target.
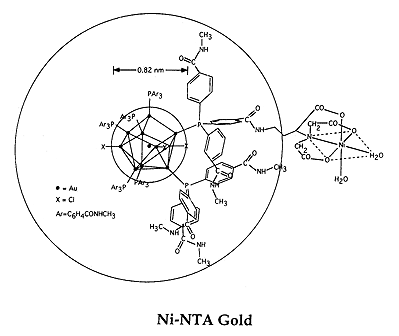
NTA-Ni (II) conjugate of undecagold.
We believe that the site-specific introduction of metal clusters into biological macromolecules may ultimately lead to the synthesis of novel materials, or molecular devices which combine both biological activity and unique catalytic or electronic properties of metal nanoparticles.
Metal Coordination Complexes in Structural Biology and Medicine
We are also pursuing other applications of metal cluster complexes and coordination compounds in the determination of biological structure and function using other techniques. We have an ongoing interest in engineering heavy atom cluster such as tetrairidium and undecagold for use as heavy-atom derivatization reagents for protein (especially membrane protein) crystallography, and in medical applications such as the targeting of metal-containing diagnostics (such as MRI imaging/contrast reagents) to sites of interest.
- "FluoroNanogold: an important probe for correlative microscopy:" Takizawa, T.; Powell, R. D.; Hainfeld, J. F., and Robinson, J.M.; J. Chem. Biol., 8, 129-142 (2015).
- "Preparation and high-resolution microscopy of gold cluster labeled nucleic acid conjugates and nanodevices:" Powell, R. D., and Hainfeld, J. F.; Micron, 42, 163-174 (2011).
- "Site-specific biomolecule labeling with gold clusters:" Ackerson, C. J.; Powell, R. D., and Hainfeld, J. F.; Methods Enzymol., 481, 195-230 (2010).
- "Nanogold Labels, Covalent Gold, and Enzyme Metallography as Components of Nanodevices:" Powell, R. D.: Hainfeld, J. F.; Gutierrez, E.; Furuya, F. R.; Joshi, V. N.; Liu, W., and Takvorian, P. M.; AIP Conf. Proc. (Fritzsche, W., and Bier, F., Eds.), 1062, 91-99 (2008).
- "In vivo immunogold labeling confirms large-scale chromatin folding motifs:" Kireev, I.; Lakonishok, M.; Liu, W.; Joshi, V. N.; Powell, R. D., and Belmont, A. S.; Nature Methods, 5, 311-313 (2008).
- "Metallographic in situ hybridization:" Powell, R. D.; Pettay, J. D.; Powell, W. C.; Roche, P. C.; Grogan, T. M.; Hainfeld, J. F., and Tubbs, R. R.; Hum. Pathol., 38, 1145-1159 (2007).
- "Enzymatic control of metal deposition as key step for a low-background electrical detection for DNA chips:" Möller, R.; Powell, R. D.; Hainfeld, J. F., and Fritzsche, W.; Nano Lett., 5, 1475-1482 (2005).
- "Gold and Silver-Facilitated Metallographic In Situ Hybridization Procedures for Detection of HER2 Gene Amplification:" Tubbs, R R.; Pettay, J.; Skacel, M.; Downs-Kelly, E.; Powell, R. D.; Hicks, D. G., and Hainfeld, J. F.; In: Molecular Morphology in Human Tissues; Hacker G.W., and Tubbs, R. R. (Eds); CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. Ch. 5, pp. 101-106 (2005).
- "Gold Cluster Labels and Related Technologies in Molecular Morphology:" Hainfeld, J. F., and Powell, R. D.; In: Molecular Morphology in Human Tissues; Hacker G.W., and Tubbs, R. R. (Eds); CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. Ch. 4, pp. 81-100 (2005).
- "Analytical Validation and Interobserver Reproducibility of EnzMet GenePro: A Second-Generation Bright-Field Metallography Assay for Concomitant Detection of HER2 Gene Status and Protein Expression in Invasive Carcinoma of the Breast:" Downs-Kelly, E.; Pettay, J.; Hicks, D.; Skacel, M.; Yoder, B.; Rybicki, L.; Myles, J.; Sreenan, J.; Roche, P.; Powell, R.; Hainfeld, J.; Grogan, T., and Tubbs, R.; Am. J. Surg. Pathol., 29, 1505-1511 (2005).
- "High-Resolution Immunophenotyping of Subcellular Compartments in Tissue Microarrays by Enzyme Metallography:" Tubbs, R.; Pettay, J.; Powell, R.; Hicks, D. G.; Roche, P.; Powell, W.; Grogan, T, and Hainfeld, J. F.; Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol., 13, 371-375 (2005).
- "Novel bright field molecular morphology methods for detection of HER2 gene amplification:" Tubbs, R.; Pettay, J.; Hicks, D.; Skacel, M.; Powell, R.; Grogan, T., and Hainfeld, J.; J. Mol. Histol., 5, 589-594 (2004).
- "Nanoparticle Molecular Labels:" Hainfeld, J. F.; Powell, R. D., and Hacker, G. W.; In: Nanobiotechnology; Mirkin, C. A., and Niemeyer, C. M. (Eds); Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany. Ch. 23, pp. 353-386 (2004).
- "Combined fluorescent and gold probes for microscopic and morphological investigations:" Powell, R. D., and Hainfeld, J. F.; In: Gold and Silver Staining: Techniques in Molecular Morphology; Hacker G. W., and Gu, J. (Eds); CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. Ch. 9, pp. 107-118 (2002).
- "Microscopic uses of Nanogold:" Hainfeld, J. F.; Powell, R. D., and Furuya, F. R.; In: Gold and Silver Staining: Techniques in Molecular Morphology; Hacker G. W., and Gu, J. (Eds); CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. Ch. 6, pp. 85-106 (2002).
- "Silver- and gold-based autometallography of Nanogold:" Powell, R. D., and Hainfeld, J. F.; In: Gold and Silver Staining: Techniques in Molecular Morphology; Hacker G. W., and Gu, J. (Eds); CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. Ch. 3, pp. 29-46 (2002).
- "Interobserver Interpretative Reproducibility of GOLDFISH, A First Generation Gold-Facilitated Auto-metallographic Bright Field In Situ Hybridization Assay for HER-2/neu Amplification in Invasive Mammary Carcinoma:" Tubbs, R.: Skacel, M.; Pettay, J.; Powell, R.; Myles, J.; Hicks, D.; Sreenan, J.; Roche, P.; Stoler, M. H., and Hainfeld, J.; Am. J. Surg. Pathol., 26, 908-913 (2002).
- "Gold-Facilitated in Situ Hybridization: A Bright-Field Autometallographic Alternative to Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization for Detection of HER-2/neu Gene Amplification:" Tubbs, R.; Pettay, J.; Skacel, M.; Powell, R.; Stoler, M.; Roche, P., and Hainfeld, J.; Am. J. Pathol., 160, 1589-1595 (2002).
- "DNA Nanowires:" Hainfeld, J. F.; ; Furuya, F. R.; Powell, R. D., and Liu, W.; Microsc. Microanal., 7, (Suppl. 2: Proceedings) (Proceedings of the Fifty-Ninth Annual Meeting, Microscopy Society of America); Bailey, G. W.; Price, R. L.; Voelkl, E., and Musselman, I. H., Eds.; Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1034-1035 (2001).
- "Gold Cluster Crystals:" Hainfeld, J. F.; Furuya, F. R., and Wall, J. S.; Microsc. Microanal., 6, (Suppl. 2: Proceedings) (Proceedings of the Fifty-Eighth Annual Meeting, Microscopy Society of America); Bailey, G. W.; McKernan, S; Price, R. L.; Walck, S. D.; Charest, P.-M., and Gauvin, R., Eds.; Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 326-327 (2000).
- "New frontiers in gold labeling:" Hainfeld, J. F., and Powell, R. D.; J. Histochem. Cytochem., 48, 471-480 (2000).
- "Greengold, a giant cluster compound of unusual eletronic structure:" Gutierrez, E.; Powell, R. D.; Furuya, F. R.; Hainfeld, J. F.; Schaaf, T. G.; Shafigullin, M. N.; Stephens, P. W., and Whetten, R. L.; Eur. J. Phys., D., 9, 647-651 (1999).
- "Giant Platinum Clusters: 2 nm Covalent Metal Cluster Labels:" Powell, R. D.; Halsey, C. M. R.; Liu, W; Joshi, V. N., and Hainfeld, J. F.; J. Struct. Biol., 127, 177-184 (1999).
- "Ni-NTA-Gold Clusters Target His-Tagged Proteins:" Hainfeld, J. F.; Liu, W.; Halsey, C. M. R.; Freimuth, P., and Powell, R. D.; J. Struct. Biol., 127, 185-198 (1999).
- "Metallosomes:" Hainfeld, J. F.; Furuya, F. R., and Powell, R. D.; J. Struct. Biol., 127, 152-160 (1999).
- "Tetrairidium, a 4-atom Cluster, is Readily Visible as a Density Label in 3D Cryo-EM Maps of Proteins at 10 - 25 Å Resolution:" Cheng, N.; Conway, J. F.; Watts, N. R.; Hainfeld, J. F.; Joshi, V.; Powell, R. D.; Stahl, S. J.; Wingfield, P. E., and Steven, A. C.; J. Struct. Biol., 127, 169-176 (1999).
- "A Covalently Linked 10 nm Gold Immunoprobe:" Gutierrez, E.; Powell, R. D.; Hainfeld, J. F., and Takvorian, P. M.; Proc. 57th Ann. Mtg., Micros. Soc. Amer.; G. W. Bailey, W. G. Jerome, S. McKernan, J. F. Mansfield, and R. L. Price (Eds.); Springer-Verlag, New York, NY; 1999, 1324-1325.
- "Combined Cy3 / Nanogold conjugates for immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization:" Powell, R. D.; Joshi, V. N.; Halsey, C. M. R.; Hainfeld, J. F.; Hacker, G. W.; Hauser-Kronberger, C.; Muss, W. H., and Takvorian, P. M.; Proc. 57th Ann. Mtg., Micros. Soc. Amer.; G. W. Bailey, W. G. Jerome, S. McKernan, J. F. Mansfield, and R. L. Price (Eds.); Springer-Verlag, New York, NY; 1999, 478-479.
- "Gold-based autometallography:" Hainfeld, J. F.; Powell, R. D.; Stein, J. K.; Hacker, G. W.; Hauser-Kronberger, C.; Cheung, A. L. M., and Schofer, C.; Proc. 57th Ann. Mtg., Micros. Soc. Amer.; G. W. Bailey, W. G. Jerome, S. McKernan, J. F. Mansfield, and R. L. Price (Eds.); Springer-Verlag, New York, NY; 1999, 486-487.
- "Ni-NTA-Nanogold for binding His tags:" Hainfeld, J. F.; Powell, R. D.; Halsey, C. M. R., and Freimuth, P.; Proc. XIV Int. Congress on Electron Microscopy, Calderon Benevides, H. A., and Jose Yacaman, M. (Eds.); Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol, UK, 1998, p. 859.
- "Combined fluorescent and gold immunoprobes: reagents and methods for correlative light and electron microscopy:" Powell, R. D.; Halsey, C. M. R., and Hainfeld, J. F.; Microscopy Research and Technique, 42, 2 (1998).
- "Dual-Labeled probes for fluorescence and electron microscopy:" Powell, R. D.; Halsey, C. M. R.; Gutierrez, E.; Hainfeld, J. F., and Furuya, F. R.; Proc. 56th Ann. Mtg., Micros. Soc. Amer.; Bailey, G. W.; Alexander, K. B.; Jerome, W. G.; Bond, M. G., and McCarthy, J. J., Eds.; Springer, New York, NY, 1998, p. 992.
- "Nanogold Technology: New frontiers in gold labeling:" Hainfeld, J. F., and Powell, R. D.; Cell Vision, 4, 408-432 (1997).
- Powell, R. D.; Halsey, Carol M. R.; Spector, D. L.; Kaurin, S. L.; McCann, J.;, and Hainfeld, J. F. A covalent fluorescent-gold immunoprobe: "simultaneous" detection of a pre-mRNA splicing factor by light and electron microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem., 45, 947-956 (1997).
- "Large Cluster and Combined Fluorescent and Gold Immunoprobes:" Powell, R. D.; Hainfeld, J. F.; Halsey, C. M. R.; Spector, D. L.; Kaurin, S.; McCann, J.; Craig, R.; Fay, F. S., and McNamara, K. E.; In Proc 54th Ann. Mtg. Micros. Soc. Amer., G. W. Bailey, J. M. Corbett, R. V. W. Dimlich, J. R. Michael and N. J., Zaluzec (Eds.). San Francisco Press, San Francisco, CA, pp. 892-893 (1996).
- "Combined fluorescent and gold nucleic acid probes:" Powell, R.D., Hainfeld, J.F., Churchill, M.E.A., and Belmont, A.S.I.; In Proc 52nd Ann. Mtg. Micros. Soc. Amer., G. Bailey and A.J. Garratt-Reed (Eds.). San Francisco Press, San Francisco, CA, pp.176-177 (1994).
- "Methylamine vanadate (NanoVan) negative stain:" Hainfeld, J.F., Safer, D., Wall, J.S., Simon, M., Lin, B., and Powell, R. D.; in In Proc. 52nd Ann. Mtg. Micros. Soc. Amer.; Bailey, G.W. and Garratt-Reed, A.J. (Eds.), San Francisco Press, San Francisco, pp. 132-133, (1994).
- "A new 1.4 nm gold-Fab probe:" Furuya, F. R., Hainfeld, J. F., and Powell, R. D.; In Proc. 49th Ann. Mtg., Micros. Soc. Amer.; Bailey, G. W., and Hall, E. L. (Eds.); San Francisco Press, San Francisco, CA, 1991, pp.286-287.
Abstracts:
- "Combined fluorescent and large metal cluster immunoprobes:" Powell, R. D.; Halsey, C. M. R.; Gutierrez, E., and Hainfeld, J. F.: Proc. 5th US-Japan Meeting of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, San Diego, July 23-26, 1998.
- "Design, synthesis, and conjugation of large metal cluster complexes as immunoprobe labels:" Powell, R. D.; Furuya, F.R.; Hainfeld, J.F., and Halsey, C.M.R.; Abstracts of 213th National Meeting, American Chemical Society, San Francisco, April 13-18, 1997 (Abstract INOR #334)
Search Me! instant Medline search (results will be displayed in a new window): one link searches Medline for my publications (Note: it will also find those of any other "Powell RD" out there. Not all of the papers it finds will be mine...thanks, National Center for Biotechnology Information / National Library of Medicine).
|



