![[Nanoprobes Tech Support (14k)]](../Images/logo_tech.gif)
Updated: November 14, 2008
GOLDENHANCE PRODUCT INFORMATION
GoldEnhanceTM LM/Blot Formulation
[GoldEnhanceTM LM/Blot Formulation product page]

| Product Name: |
GoldEnhance - LM/Blot Formulation |
| Catalog Number: |
2112 |
| Appearance: |
Colorless solution |
| Revision: |
1.5 (January 2009) |
Technical Assistance Online
![[2112-PDF]](../Images/pdf.gif) Instructions (PDF) Instructions (PDF)
![[2112-PDF]](../Images/pdf.gif) Material Safety Data Sheet (PDF) Material Safety Data Sheet (PDF)
- Introduction
- Product Information
- Gold Enhancement for Light Microscopy
- Gold Enhancement for Immunoblots and Membrane Blots
- Gold Enhancement for EM
- References
This novel, high-quality autometallographic enhancement reagent may be used in the same manner as conventional silver enhancement reagents. However, instead of depositing silver, this product selectively deposits gold onto Nanogold® particles or colloidal gold particles.1-4
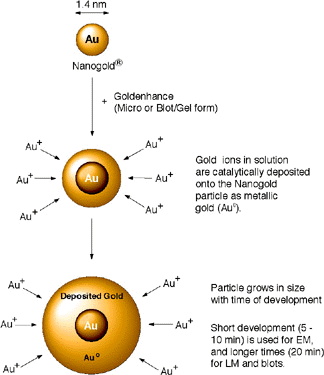
Figure 1: Enlargement of Nanogold® with GoldEnhance.
|
Why gold? Gold has several important advantages for electron microscopy, light microscopy and membrane blotting:
- Very sensitive detection with low background.
- Autonucleation is minimal even after 1-2 hours - more convenient for multiple samples, or if sample access is restricted (e.g. automated processing).
- High resolution.
- Much faster than chemiluminescence.
- Low viscosity for easy and accurate mixing of components.
- Milder pH conditions than silver enhancement: Goldenhance is used at near neutral pH, and you can adjust the pH for better sample preservation.
- Can be used in physiological buffers - gold is not precipitated as silver is (however, rinsing with water first is still recommended).
- Permanent staining: does not fade.
- No autofluorescence or quenching.
- Observe with brightfield optics - simpler and less expensive than fluorescence.
- Excellent shelf life.
|
This reagent consists of 15 mL Solution A (enhancer), 15 mL Solution B (activator), 15 mL Solution C (initiator) and 15 mL of Solution D (buffer), sufficient for up to 200 slides (using 80 L per specimen). The reagent is formed by combining equal volumes of the enhancer and activator, and then adding the initiator. The mixture should be prepared immediately before use. For optimum results, we recommend waiting 5-10 minutes after mixing A and B before adding C and D, although the the reagent will produce successful enhancement if C and D are added immediately or up to two hours later. Nanogold® or colloidal gold nucleates deposition of gold to give electron-dense enlarged colloidal particles in the electron microscope, or a dense black signal by light microscopy or in blots.
Please Note: This formulation is intended principally for light microscopy and membrane blotting. The alternative EM formulation (catalog number 2113) is optimized for EM use.
The time period for optimum gold enhancement varies with application, but 10 to 20 minutes has been found to be optimal for light microscopy with tissue sections, while 20 to 30 minutes is highly effective for blots.
Store the component solutions at 4°C. Avoid cross-contamination of the solutions: to prevent replacing the caps on the wrong bottles, the cap of the Solution A (enhancer) is green and that of the Solution B (activator) is yellow, while that of Solution C (initiator) is purple and that of Solution D (buffer) is white. Avoid skin contact.
Warning: For research use only. Not recommended or intended for diagnosis of disease in humans or animals. Do not use internally or externally in humans or animals.
Note: All components should be equilibrated to room temperature prior to the enhancement procedure.
Contents
GoldEnhance is prepared immediately before use by mixing equal amounts of Solution A (enhancer) and Solution B (activator), followed by the Solution C (initiator), and Solution D (buffer). For optimum results, we recommend waiting 5-10 minutes after mixing A and B before adding C and D, although the the reagent will produce successful enhancement if C and D are added immediately to up to two hours later. The reagents are supplied in dropping bottles for easier dispensing of small amounts.
If aldehyde-containing reagents have been used for fixation, it is receommended that these be quenched before labeling. This may be achieved by incubating the specimens for 5 minutes in 50 mM glycine solution in PBS (pH 7.4); ammonium chloride (50 mM) or sodium borohydride (0.5 - 1 mg/ml) in PBS may be used instead of glycine.
The following procedure was developed for gold enhancement of In Situ hybridization specimens by Hacker et al. as a modification of the Nanogold®-Silver Staining procedure.1,5 It has been found to be effective for enhancement of tissue sections for light microscope observation. We have found times of 10-20 minutes give optimal results; however, this reagent is intended to function in a wide range of conditions, and different washes and development times may give better results in your application. You should follow your normal procedure up to the application of the gold conjugate; the protocol below describes the steps after this:
- Incubate the sections with Nanogold® or colloidal gold conjugate according to current protocols or using the buffers, concentrations and protocols recommended for the conjugate.
- Wash in PBS pH 7.6, 2 times 5 min each.
- Wash in PBS-gelatin pH 7.6 for 5 min.
- Repeatedly wash in distilled water for at least 10 min altogether, the last 2 rinses in ultrapure water (EM-grade).
- Prepare GoldEnhanceTM using equal amounts of the four components (Solutions A,B,C, and D); prepare about 80 microliters per slide.
- Dispense Solution A (enhancer: green cap) into a clean tube or dish, add Solution B (activator: yellow cap), and mix thoroughly.
- Wait 5 minutes.
- Add Solution C (initiator: purple cap) and Solution D (buffer) and mix thoroughly.
- Apply 1-2 drops (~ 80 µL, sufficient to cover the specimen) to the slide.
- Develop specimen for 10 - 20 minutes. More or less time can be used to control particle size and intensity of signal.
- When optimum staining is reached, immediately stop by rinsing carefully with deionized water.
|
PBS-Gelatin Buffer:
|
PBS Buffer:
- 20 mM phosphate
- 150 mM NaCl
- pH 7.6
|
Notes:
- Development starts with addition of Solution C (initiator), so apply to sample as soon as possible after adding C and D to minimize autonucleation background.
- To obtain an especially dark signal, or for further development, develop longer or gold enhancement may be revitalized with a freshly mixed portion of GoldEnhance (rinse with distilled ater between applications of GoldEnhance).
- The development is not highly light sensitive, so may be conducted under normal room lighting, or viewing by light microscopy.
- Some users reported good development omitting the use of Solution D (buffer), but deposition times are then slower.
Contents
The basic procedure for gold immunoblotting has been described by Moeremans et al;6 the following procedure is adapted from this protocol. GoldEnhanceTM is prepared immediately before use by mixing equal amounts of the Solution A (enhancer) and Solution B (activator), Solution C (initiator) and Solution D (buffer). Mix Solution A (enhancer) and Solution B (activator) thoroughly, wait 5 min, then add Solution C (initiator) and Solution D (buffer) and mix thoroughly again. The reagents are supplied in dropping bottles for easier dispensing of the same amounts. We have found a development time of 20-30 minutes to be effective; however, this reagent is intended to function in a wide range of conditions, and your experiments may require different times or reagents. Development times and the appearance of background signal may vary with the type of gold probe used, and with the type of membrane used for blotting.
The target should be blotted onto the membrane, then detected with the primary probe according to the usual procedure. You should follow your usual or recommended protocol up to the application of the Nanogold® or immunogold reagent, then proceed with the following steps; also see Notes, above. Formulations of ancillary buffers 1 and 2 are given after the procedure.
- Incubate with a 1/100 to 1/500 dilution of the NANOGOLD® reagent or colloidal gold conjugate in according to current or recommended protocols.
- Rinse with buffer 1 (3 X 5 mins), then buffer 2 (2 X 5 mins).
- OPTIONAL (may improve sensitivity): Postfix with glutaraldehyde, 1 % in buffer 2 (10 mins).
- Rinse with deionized water (2 X 5 mins).
- Prepare GoldEnhance using equal amounts of the four components (Solutions A,B,C, and D).
- Dispense Solution A (enhancer: green cap) into a clean tube or dish, add Solution B (activator: yellow cap), and mix thoroughly.
- Wait 5 minutes.
- Add Solution C (initiator: purple cap) and Solution D (buffer) and mix thoroughly.
- Apply solution to cover the blot.
- Develop specimen for 20 - 30 minutes. More or less time can be used to control particle size and intensity of signal.
- Rinse repeatedly with deionized water.
Buffer 1:
- 20 mM phosphate
- 150 mM NaCl
- pH 7.4
- 0.8% BSA (bovine serum albumin)
- 2 mM sodium azide (NaN3)
|
Buffer 2 (PBS):
- 20 mM phosphate
- 150 mM NaCl
- pH 7.4
|
Contents
This reagent is optimized for light microscopy and membrane blotting rather than for electron microscopy. For electron microscopy applications, we recommend that you use Goldenhance EM (catalog number 2113) which is optimized for EM use. However, this reagent (2112) may also be used for electron microscopy, particularly if larger particles are desired or a high labeling density is anticipated.1,2
Contents
- Powell, R. D., and Hainfeld, J. F.: Silver- and gold-based autometallography of Nanogold. In: Gold and Silver Staining: Techniques in Molecular Morphology; Hacker G. W., and Gu, J. (Eds): CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, ch. 3, pp. 29-46 (2002).
- Hainfeld, J. F.; Powell, R. D.; Stein, J. K.; Hacker, G. W.; Hauser-Kronberger, C.; Cheung, A. L. M., and Schofer, C.: Gold-based autometallography; Microsc. Microanal., 5, (Suppl. 2: Proceedings); G. W. Bailey, W. G. Jerome, S. McKernan, J. F. Mansfield, and R. L. Price (Eds.); Springer-Verlag, New York, NY; 486-487 (1999) (paper).
- Ackerley, C. A.; Tilups, A.; Bear, C. E., and Becker, L. E.: Correlative LM/TEM studies are essential in evaluating the effectiveness of liposome mediated delivery of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) as a corrective therapy in a CFTR knockout mouse that develops lung disease. Microsc. Microanal., 5, (Suppl. 2: Proceedings); G. W. Bailey, W. G. Jerome, S. McKernan, J. F. Mansfield, and R. L. Price (Eds.); Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 484-485 (1999).
- Powell, R. D.; Joshi, V. N.; Halsey, C. M. R.; Hainfeld, J. F.; Hacker, G. W.; Hauser-Kronberger, C.; Muss, W. H., and Takvorian, P. M.: Combined Cy3 / Nanogold Conjugates for Immunocytochemistry and In Situ Hybridization. Microsc. Microanal., 5, (Suppl. 2: Proceedings); G. W. Bailey, W. G. Jerome, S. McKernan, J. F. Mansfield, and R. L. Price (Eds.); Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 478-479 (1999).
- Graf, A. H.; Cheung, A. L.; Hauser-Kornberger, C.; Dandachi, N.; Tubbs, R. R.; Dietze, O., and Hacker, G. W.: Clinical relevance of HPV 16/18 testing methods in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Molecul. Morphol., 8, 300-309 (2000).; Tubbs, R.; Pettay, J.; Skacel, M.; Powell, R.; Stoler, M.; Roche, P., and Hainfeld, J.: Gold-Facilitated in Situ Hybridization: A Bright-Field Autometallographic Alternative to Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization for Detection of HER-2/neu Gene Amplification. Am. J. Pathol., 160, 1589-1595 (2002).
- Moeremans, M.; Daneels, G.; Van Dijck, A.; Langanger, G., and De Mey, J.: Sensitive visualization of antigen-antibody reactions in dot and blot immune overlay assays with immunogold and immunogold/silver staining. J. Immunol. Meth., 74, 353-360 (1984).
Technical Assistance Available.
For a complete list of references citing this product, please visit our References page.
Contents
|