 |
Nanoprobes, Incorporated
95 Horseblock Road, Unit 1, Yaphank, NY 11980-9710
Tel: (877) 447-6266 (Toll-Free in US) or (631) 205-9490 | Fax: (631) 205-9493
tech@nanoprobes.com | www.nanoprobes.com |
Updated: February, 2011
NANOPROBES PRODUCT INFORMATION
| Product Name: |
AuroVist™-15nm Gold Nanoparticle X-ray Contrast Agent |
| Catalog Number: |
1115 |
| Appearance: |
Red Liquid |
| Quantity: |
40 mg Au in the form of biocompatible 15 nm gold
nanoparticles |
| Revision: |
1.0 (February 2011) |
Technical Assistance Online
![[2025-PDF]](../Images/pdf.gif) Instructions (PDF) Instructions (PDF)
![[2025-PDF]](../Images/pdf.gif) MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheet (PDF) MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheet (PDF)
AuroVist™: The first Gold Nanoparticle X-ray Contrast Agent for in vivo* use
Introduction
AuroVist™1 is a novel nanotechnology contrast agent based on gold nanoparticles, the first of its kind to be commercially available. AuroVist™ enables greatly enhanced X-ray imaging of blood vessels, tumors, and other biological systems and organs. AuroVist™-15 nm consists of gold nanoparticles with a core diameter of 15 nm, stabilized with a highly water soluble organic shell. This makes them useable at high concentrations (up to at least 200 mg Au/cc) and well tolerated by animals even at high concentrations (LD50 > 5 g Au/kg).
Some of the significant unique features and advantages of AuroVist™-15 nm include:
-
Longer blood residence time than iodine agents (~15 hr blood half-life).
- High Contrast (>1,000 HU initial blood contrast; 40 mg in a 20g mouse).
- Does not clear through kidneys (for kidney imaging use AuroVist™-1.9nm, #1102).
- Low toxicity (LD50> 5 g Au/kg).
-
Can achieve higher contrast than standard iodine agents
(Gold absorbs ~3 times more than an equal weight of iodine at 20 and 100 keV).
- Low osmolality, even at high concentrations.
- Low viscosity, similar to water; easy to inject with minimal trauma, even into small blood vessels.
- Can be imaged using standard MicroCT, clinical CT, planar X-ray, or mammography.
- Enhances radiotherapy dose.2
AuroVist™ is particularly useful for MicroCT animal imaging, such as in vivo vascular casting,3 studies of tumors, stroke, atherosclerosis and other vascular conditions.
*not approved for human use.
Contents
Each vial of AuroVist™-15 nm contains 40 mg of gold in the form of 15 nm gold nanoparticles (note this is the weight of gold metal, and does not include the coordinated ligand shell around the gold core). It is supplied at a concentration of 200 mg Au/mL in 0.2 mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS: 20 mM sodium phosphate with 150 mM sodium chloride, pH 7.4), filtered through a 0.22 µm filter.
Physical Properties
The 15 nm gold nanoparticles are red in color and soluble in aqueous solutions. They may be dried and dissolved in some organic solvents. For purification or exchange into other solvents, they may be centrifuged: they form a pellet when spun on a tabletop Eppendorf microfuge at 16,000 x g for 12 minutes.
Storage
This product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, the AuroVist™-15 nm gold nanoparticle solution should be stored at 4°C.
Instructions for Use
AuroVist™-15nm solution should be diluted to the required concentration in PBS (20 mM sodium phosphate with 150 mM sodium chloride, pH 7.4), or other buffer if desired. A typical volume for intravenous injection into a mouse (for example into the tail vein), is 0.2 mL. Since the LD50 is > 5 g Au/kg, a 20 g mouse may be injected with 100 mg of gold or more.
Vascular Imaging:
Visualization of blood vessels by X-rays is best just after injection (Fig 1), but gives good imaging even hours later. The highest blood concentration is immediately after injection.
Figure 1:
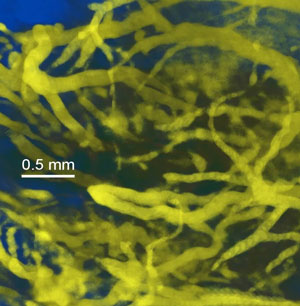 |
| High resolution vascular imaging of blood vessels in a live mouse after iv injection of AuroVist™-15. |
Tumor Imaging:
Because of its larger size, AuroVist™-15 nm does not significantly leak out of normal vasculature, as do standard iodine contrast agents such as iohexol (Omnipaque® molecular weight 821). However, it has been documented that nanoparticles exit leaky tumor neovasculature through the "Enhanced Permeability and Retention" (EPR) effect. The gold nanoparticles leak into tumors and are retained there, particularly at the growing edge tumor periphery, and build up over ~10-24 hours. Through this mechanism, AuroVist™-15nm may be selectively taken up by tumors (Fig. 2).
Figure 2:
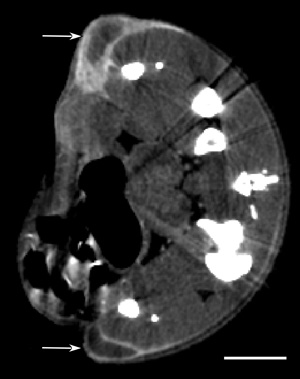 |
| MicroCT section of mouse with two subcutaneous tumors (one one each leg, arrows) showing AuroVist™-15 nm uptake 20 hours after intraveneous injection. Bar = 5 mm. |
Tips for Best Imaging Results with AuroVist™
X-ray Properties of Gold:
Gold (Z=79, Atomic weight = 197) absorbs X-rays as shown in Fig. 3.
Figure 3:
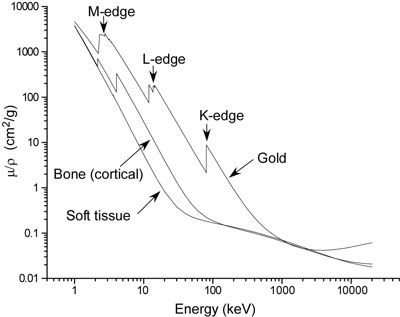 |
| X-ray absorption of gold, bone and soft tissue vs. X-ray energy.
|
The absorption increases by a significant factor (jump ratio) above its L and K edges (Table 1).
Table 1:
|
Absorption
Edge
|
Energy (keV)
|
µ/ρ (cm2/g)
|
jump ratio
|
|
|
11.8
|
75.8
|
|
|
L3
|
11.9
|
187.0
|
2.5
|
|
|
13.6
|
128.3
|
|
|
L2
|
13.7
|
176.4
|
1.4
|
|
|
14.3
|
158.8
|
|
|
L1
|
14.4
|
183.0
|
1.2
|
|
|
80.6
|
2.1
|
|
|
K
|
80.7
|
8.9
|
4.2
|
| Table 1: X-ray absorption properties of gold. |
It is therefore advantageous to image using these absorptions. MicroCT units generally allow various "kVp" energies to be selected. kVp means kilovolt peak and denotes the highest output energy. Electrons accelerated to this voltage hit a (e.g., tungsten) target and x-rays are emitted via bremsstrahlung (or stopping radiation). Actually, there is 0 intensity at the kVp and 0 at 0 kV, with a broad spectrum in between, with a median energy about 1/3 of the peak energy (kVp). Since gold has a favorable absorption at the K and L energies, one would use ~3 times this for the kVp. For L=14 keV, the unit should be set to ~ 3x14 = 42 kVp.
X-ray Instruments:
Tips for imaging with AuroVist™
Mammography:
These instruments are suitable for small animal imaging. Use of lower kVp (e.g., 22 kVp) is recommended to take advantage of the L edge Au absorptions. Exposures are typically 1 sec or less for a mouse, so live imaging is possible. Resolution can be < 0.1 mm.
Clinical CT:
80 kVp gives the greatest attenuation, but higher voltages, particularly with filtering can make use of the Au K edge. Imaging time is typically a few seconds, with resolution ~0.3 mm.
MicroCT:
Here the resolution is increased (to even 2 microns), but the tube power is typically ~100 times less than a clinical unit. Fine area 2D detectors mean that many tiny pixels must each receive enough counts. This then requires a much longer imaging time (e.g., 20 min-2 hours) than clinical CT (a few sec). Many units also slow the tube rotation down such that only 1 revolution is done in the selected imaging time (e.g., 1 hour). If the animal moves during collection of this data set, the back projection 3D reconstruction will be errant. This places significant constraints for live animal imaging, and motion must be minimized, such as breathing and heartbeat (mouse = 600 beats/min). A simple solution is to kill the animal some time after injection and then image, but live imaging has been accomplished if the region can be gated or immobilized during the imaging time.
Injection Recommendations
Avoiding Acute Toxicity
Certain strains of mice appear to be more or less tolerant of this gold. Until tested, it is recommended to use a lower injected amount.
Tips on intraveneous injection
For mice, inject into the tail vein with a volume of ~0.2 mL. 40mg/0.2mL is equivalent to 200 mg Au/mL, AuroVist is intensely dark, and immediately during or after injection, one should see the skin, ears, eyes, and paws become darker red or purple due to the gold in all the blood vessels. During injection, you should feel no resistance. If it is hard to inject, or a large amount of gold accumulates at the point of injection, the vein was missed. If you feel resistance to injection, stop immediately and try again elsewhere or later. Warming the tail helps dilate the veins.
- Hainfeld, J. F.; Slatkin, D. N.; Focella, T. M, and Smilowitz, H. M.: Gold nanoparticles: a new X-ray contrast agent. Br. J. Radiol., 79, 248-253 (2006). [Full article]
- Hainfeld, J. F., Slatkin, D. N., and Smilowitz, H. M.: The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys. Med. Biol., 49, N309-N315 (2004). [Abstract]
- Hainfeld, J. F.; Slatkin, D. N.; Focella, T. M., and Smilowitz, H. M.: In Vivo Vascular Casting. Microsc. Microanal., 11, (Suppl. 2: Proceedings); Price, R.; Kotula, P.; Marko, M.; Scott, J. H.; Vander Voort, G. F.; Nanilova, E.; Mah Lee Ng, M.; Smith, K.; Griffin, P.; Smith, P., and McKernan, S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, p. 1216CD (2005). [Full article]
Questions? Technical Support is available. Drop us a line-- we're here to help.
 |
Nanoprobes, Incorporated
95 Horseblock Road, Unit 1, Yaphank, NY 11980-9710
Tel: (877) 447-6266 (Toll-Free in US) or (631) 205-9490 | Fax: (631) 205-9493
tech@nanoprobes.com | www.nanoprobes.com |
|




